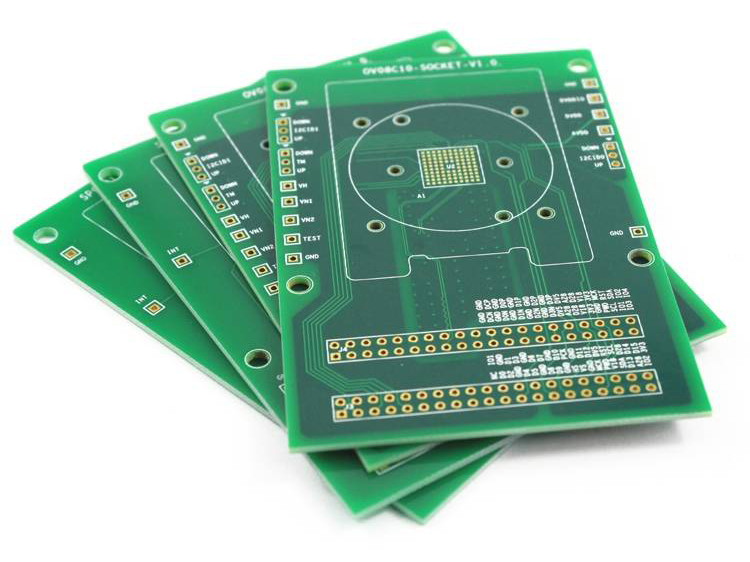
The electronics revolution has shaped the present day world, and at the centre of this change is the humble printed circuit board (PCB). PCBs are indispensably to about each electronic gadget, from smart phones to industrial machinery. As the request for more proficient and compact gadgets develops, headways in circuit board fabricating and manufacture strategies are continually advancing. Flexible PCBs are too picking up noticeable quality, advertising arrangements for energetic and compact applications. This Blog plunges profound into the complexities of PCB board manufacture, investigates the part of PCB manufacture producers, and highlights the significance of Flexible PCBs in today’s tech-driven landscape.
What is Printed Circuit Board Manufacturing?
Printed Circuit board manufacturing is the prepare of planning, creating, and gathering PCBs. A PCB mechanically bolsters and electrically interfaces components utilizing conductive pathways, tracks, and cushions made from copper sheets covered onto a non-conductive substrate.
Key Components of Circuit Board Manufacturing:
1. Design Phase
Using plan computer program such as Falcon, KiCad, or Altium, engineers make the schematic and format of the PCB.
Design for manufacturability (DFM) standards are connected to guarantee the board can be delivered effectively and cost-effectively.
2. Material Selection
Common substrates incorporate FR4 (a fiberglass-reinforced epoxy cover), ceramic, and polyimide for Flexible PCBs.
The sort of substrate depends on the application’s electrical, warm, and mechanical requirements.
3. Photolithography
A photoresist layer is connected to the copper-clad board and uncovered to UV light utilizing a stencil of the PCB design.
This handle makes a difference characterize the circuit pattern.
4. Etching
The uncovered copper is evacuated utilizing chemical arrangements, clearing out behind the craved circuit pathways.
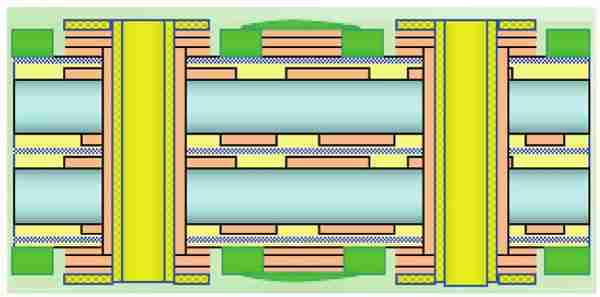
5. Layering (for Multilayer PCBs)
Multiple layers of circuits are fortified together with protection materials between them. This handle includes exact arrangement and pressing.
6. Drilling
Holes are bored for vias and through-hole components. Progressed laser boring guarantees tall precision.
7. Plating
Electroplating coats the gaps and pathways with conductive materials like copper to make electrical connections.
8. Solder Mask Application
A defensive patch cover layer is connected to anticipate oxidation and patch bridging.
9. Silkscreen Printing
Labels, component markers, and other identifiers are printed on the board utilizing silkscreen techniques.
10. Testing
Electrical testing guarantees that all associations are utilitarian and meet specifications.
PCB Board Manufacture: An Overview
PCB fabrication includes turning the plan into a physical board prepared for gathering. Not at all like the get together stage, which includes setting components on the board, manufacture centres exclusively on making the PCB.
Types of PCB Boards:
1. Single-Sided PCBs
Components and conductive tracks are on one side of the board.
Used in basic gadgets like calculators.
2. Double-Sided PCBs
Tracks and components are on both sides, with vias interfacing layers.
Found in more complex gadgets like Driven frameworks and control supplies.
3. Multilayer PCBs
These sheets have three or more conductive layers.
Common in progressed gadgets like smart phones and restorative devices.
4. Rigid PCBs
Made from unbendable materials, they are tough and durable.
Used in applications where inflexibility is crucial.
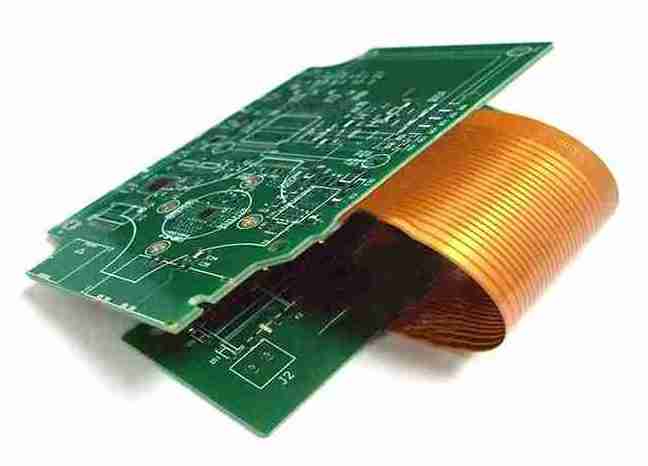
5. Flexible PCBs
Made from materials like polyimide, these sheets can twist and fold.
Ideal for compact and energetic applications like wearable’s and car systems.
6. Rigid-Flex PCBs
A combination of unbending and Flexible areas, advertising flexibility in design.
Fabrication Steps
The creation prepare builds on the fabricating steps but is custom fitted to the sort of PCB being created. Progressed methods such as laser imaging, controlled impedance testing, and smaller scale through arrangement are utilized for complex boards.
Innovations Driving PCB Manufacturing Forward
The PCB fabricating industry is experiencing a innovative renaissance, with advancements that guarantee more prominent productivity, accuracy, and adaptability.
1. Embedded Components
Traditional PCBs have components mounted on their surface, but inserted component innovation coordinating these straightforwardly into the PCB layers. This comes about in:
• Reduced board size.
• Enhanced unwavering quality by dispensing with patch joints.
• Improved electrical performance.
2. Progressed Testing Methods
Automated optical inspection (AOI) and mechanized X-ray inspection (AXI) have ended up standard in quality affirmation, enabling:
• Detection of tiny defects.
• Verification of multilayer alignment.
• Identification of voids and irregularities in soldering.
3. Microvia Technology
Microvias, little gaps utilized to interface layers, are basic in high-density PCBs. Laser boring innovation has revolutionized the creation of microvias, permitting for:
• Greater circuit density.
• Reduced flag misfortune in high-speed applications.
4. Flexible Hybrid Electronics (FHE)
Combining Flexible PCBs with printed hardware, FHE empowers the integration of sensors, control sources, and communication modules into Flexible designs. Applications incorporate wearable gadgets, shrewd materials, and healthcare checking systems.
5. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in PCB Design
AI-driven plan devices optimize PCB formats for execution and manufacturability, coming about in:
• Reduced plan cycles.
• Enhanced warm and flag integrity.
• Minimized chance of plan errors.
The Role of PCB Fabrication Manufacturers
PCB manufacture producers play a basic part in the gadgets supply chain. They interpret plans into high-quality, utilitarian circuit sheets. The best producers center on accuracy, versatility, and quality assurance.
Key Contemplations When Choosing a PCB Manufacturer:
1. Capabilities
Check if the producer bolsters progressed highlights like multilayer sheets, Flexible PCBs, and high-frequency materials.
2. Quality Standards
Certifications like ISO 9001, IPC-A-610, and RoHS compliance show tall fabricating standards.
3. Prototyping Services
Quick-turn prototyping makes a difference test plans some time recently full-scale production.
4. Lead Times
Efficient producers convey inside stipulated timelines without compromising quality.
5. Customization
Look for producers who can handle custom necessities like special shapes or particular fabric needs.
6. Testing Facilities
Ensure the producer performs electrical testing, X-ray assessment, and other quality checks.
7. Cost Efficiency
Competitive estimating without relinquishing quality is fundamental for commercial viability.
Innovations by Driving Manufacturers:
• Adoption of computerization in penetrating and carving processes.
• Use of Industry 4.0 advances for real-time monitoring.
• Integration of eco-friendly hones to minimize waste.
Challenges in PCB Fabrication
Despite headways, PCB
fabrication faces a few challenges that producers must overcome to stay competitive.
1. Miniaturization
The request for littler, more slender, and lighter PCBs pushes the limits of current fabricating procedures. Keeping up flag keenness in thickly stuffed circuits is a critical challenge.
2. Thermal Management
As gadgets gotten to be more capable, overseeing warm dissemination gets to be basic. Imaginative arrangements, such as warm vias and progressed heat-sinking materials, are essential.
3. Wastage in the Supply Chain
Global disturbances caused by epidemics or geopolitical pressures affect the availability of raw materials and resources. Producers are differentiating their supply chains to relieve risks.
4. High-Frequency Applications
The rise of 5G and progressed communication frameworks requests PCBs that can handle high-frequency signals with negligible misfortune. This requires specialized materials and exact manufacture processes.
5. Natural Concerns
Adopting economical hones whereas keeping up productivity is a adjusting act for numerous manufacturers.
The Growing Demand for Custom PCBs
Custom PCBs are outlined to meet particular application prerequisites, advertising custom fitted arrangements for one of a kind challenges.
Advantages of Custom PCBs:
1. Optimized Performance
Designs are fine-tuned for particular working conditions, guaranteeing most extreme efficiency.
2. Space Savings
Custom shapes and sizes permit superior utilization of space inside the device.
3. Reduced Costs
Eliminates superfluous highlights, decreasing fabric and generation costs.
4. Enhanced Aesthetics
Custom silkscreens and formats can progress the visual offer of buyer electronics.
Industries Driving the Request for Custom PCBs:
• Healthcare: Implantable gadgets, symptomatic equipment.
• Automotive: Electric vehicles, advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
• Aerospace: Satellites, flying systems.
• Industrial Automation: Mechanical autonomy, sensors.
The Future of PCB Fabrication
The future of PCB creation is molded by the merging of cutting-edge innovations and moving showcase demands.
1. Hyper-Miniaturization
As wearable gadgets and IoT applications multiply, PCBs will proceed to shrivel, consolidating progressed materials and techniques.
2. Biocompatible PCBs
Medical gadgets will require PCBs made from materials that are secure for utilize interior the human body, opening unused wildernesses in bioelectronics.
3. Quantum Computing
Quantum computers request PCBs with extraordinary flag astuteness and the capacity to work at greatly moo temperatures.
4. Integration with Rising Technologies
PCBs will progressively coordinated with advances like increased reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and independent systems.
5. Maintainability at the Forefront
Increase advertising of energy-efficient, recyclable, and biodegradable PCBs, in line with global animal capacity goals..
Flexible PCBs: The Future of Circuit Boards
Flexible PCBs are revolutionizing the design and use of devices. Their capacity to twist, bend, and accommodate to non-standard shapes makes them vital in cutting edge devices.
What Are Flexible PCBs?
Flexible PCBs use materials such as polyimide or polyester films as their substrates, allowing them to bend or break without breaking.
Advantages of Flexible PCBs:
1. Space Efficiency
Ideal for compact plans as they can fit into tight spaces.
2. Durability
Resistant to vibrations, stuns, and natural stress.
3. Lightweight
Reduces the generally weight of the device.
4. Improved Performance
Reduces the number of connectors and interconnects, progressing reliability.
5. Versatility
Can be utilized in energetic or moving applications.
Applications of Flexible PCBs:
• Consumer Gadgets: Smartphone, tablets, wearable’s.
• Automotive: Sensors, lighting frameworks, infotainment modules.
• Medical Gadgets: Pacemakers, imaging equipment.
• Aerospace: Satellites, aeronautics systems.
Challenges in Fabricating Flexible PCBs:
1. Material Handling
Flexible substrates require cautious taking care of to avoid tearing.
2. Cost
Higher fabric costs compared to unbending boards.
3. Design Complexity
Requires specialized computer program and expertise.
4. Thermal Management
Ensuring productive warm dissemination in Flexible applications.
The Impact of Emerging Technologies
Advances in innovation are forming the future of PCB fabricating and Flexible PCBs.
1. Miniaturization
As gadgets gotten to be littler, PCBs must adjust to incorporate more usefulness in less space.
2. High-Density Interconnect (HDI) PCBs
HDI sheets bolster more components and associations per square inch.
3. 3D Printing
Additive fabricating methods are being investigated for prototyping and low-volume production.
4. Advanced Materials
Graphene and other conductive materials guarantee way better execution and durability.
5. IoT Integration
PCBs outlined for IoT gadgets require remote communication capabilities and moo control consumption.
Conclusion
Circuit board manufacturing, PCB manufacturing, and increasingly flexible PCBs are at the core of modern advances in hardware. The industry continues to evolve, with a need for compact, high-performance and robust equipment. Whether it’s a basic single-sided board or a complex Flexible PCB, each sort plays a crucial part in powering today’s technology.
Selecting the right PCB fabrication manufacturer and grasping developing patterns will guarantee that businesses stay competitive in this quickly advancing field. As Flexible PCBs pick up unmistakable quality, they hold the potential to rethink how hardware are outlined and conveyed over industries.
For businesses and engineers exploring this energetic scene, understanding the complexities of PCB fabricating and collaborating with solid PCB manufacture producers is essential. The future is shinning for PCBs as they proceed to drive advance in hardware, powering a world of interminable conceivable outcomes. The travel of a PCB, from plan to a completely utilitarian board, is a confirmation to human inventiveness and the tenacious interest of mechanical brilliance. With the ever-growing request for more brilliant, speedier, and more productive gadgets, the future of PCB fabricating looks brighter than ever.