DIP production process in PCBA factories
Introduce
The manufacture of electronic components is a complex and precise process, among which DIP (dual in-line package) technology is one of the common electronic component manufacturing methods.
The DIP production process involves multiple steps, from the ready of raw materials to the final testing and packaging. This step requires professional technology and quality management.
This article will introduce the main DIP production flow in detail to better understand DIP production.
Step 1: Raw material preparation
Generally speaking, these raw materials include semiconductor chips, wires, packaging materials, and other necessary components.
At this stage, it is necessary to ensure that the quality and specifications of the raw materials meet the requirements of the product.
It is particularly noteworthy that the semiconductor chip (IC chip) plays a key role in DIP packaging, so its quality is crucial.
In order to ensure the reliability and performance of the final product, the selection and procurement process of raw materials requires strict quality control.
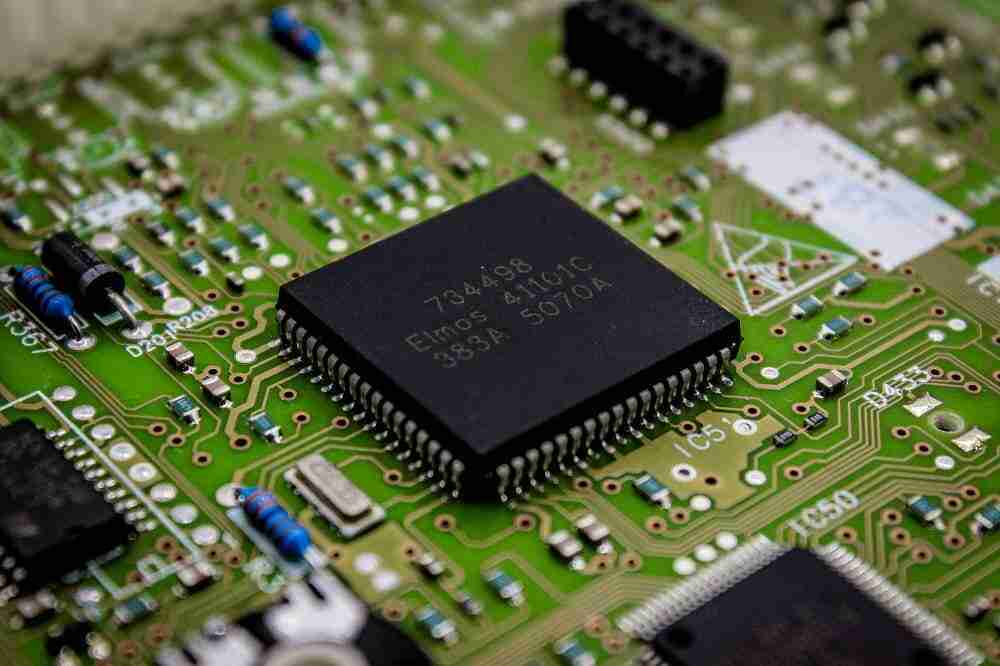
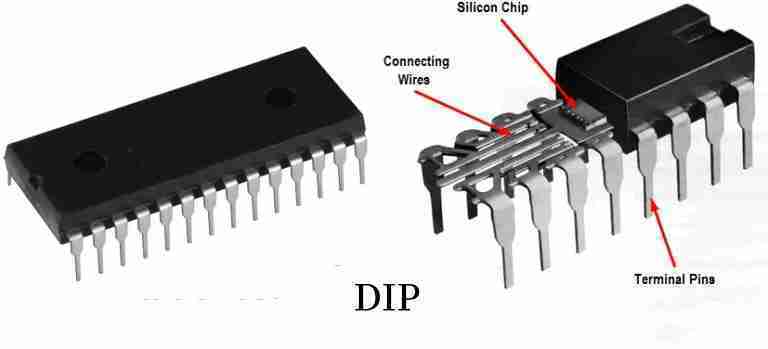
Step 2: DIP Chip packaging
Once the raw materials are ready, chip packaging will start. The semiconductor chip will be mounted into the DIP package.
It involves attaching the chip to wires and other connectors to connect it to the circuit board.
DIP packaged chips require high precision and expertise, with strict quality checks to ensure that connections are correct and there are no shorts or opens.
Step 3: Soldering
Next is the soldering stage. We will solder the DIP packaging chip to the circuit board.
It requires connecting the terminals of the wires with the pads so that current can flow through the circuit.
The welding process requires special welding equipment and materials to ensure the stability and reliability of the welding points.
Once soldering is complete, the circuit boards are sent to the next stage for inspection.
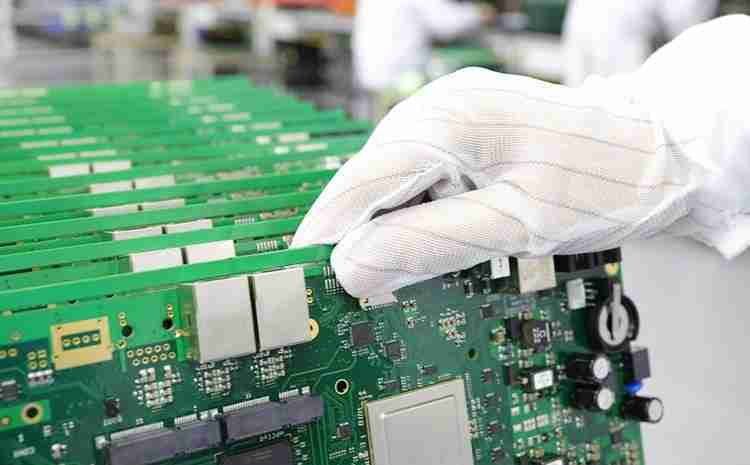
Step 4: Quality Control and Sample Testing
At every stage of DIP production, it is necessary to ensure that the product quality and performance meet the specifications.
During the quality control process, sample testing includes electrical testing, functional testing, and appearance inspection.
Electrical testing checks that connections on a printed circuit board are correct.
Functional testing verifies whether the product works properly according to the design requirements.
Appearance inspection checks whether the appearance of the product meets the standards.
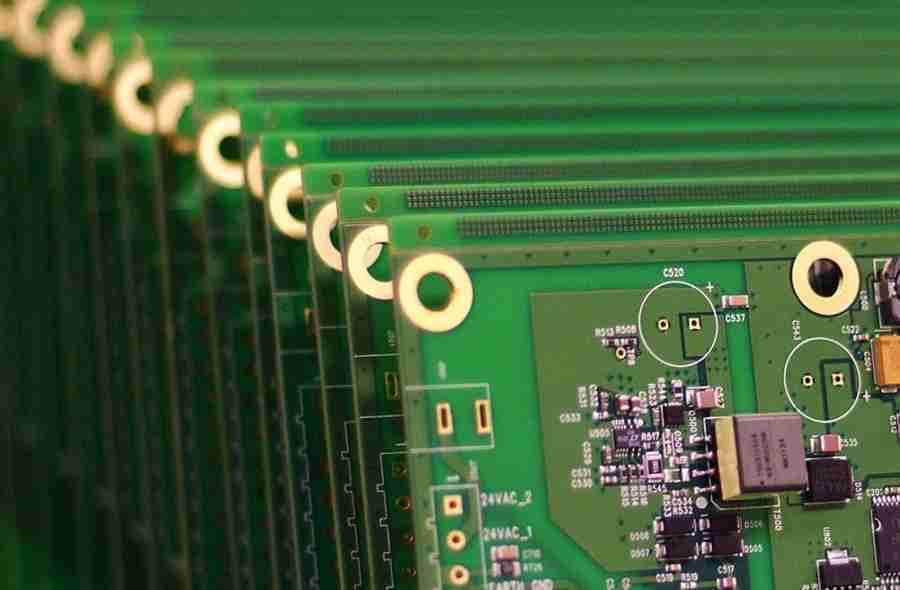
Step 5: high-volume production and final testing
The last step in mass production is final testing.
DIP products require more strict testing to ensure their performance and reliability.
These tests include temperature tests, humidity tests, vibration tests, long-term operation tests, etc.
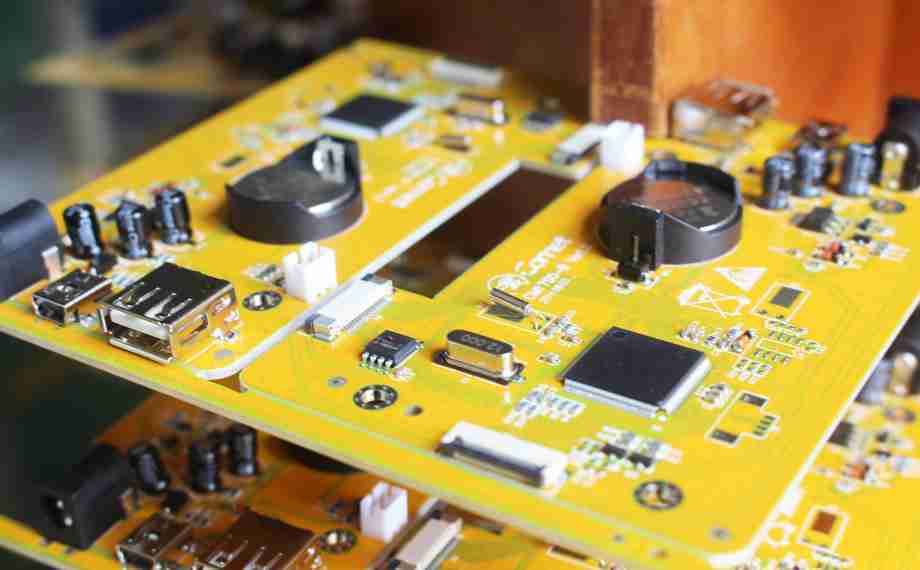
Step 6: Packing and Shipping
Once the product passes final testing, it is ready for packaging and shipment.
Here,Circuitcardassembly DIP product packaging is usually box or reel packaging, which is easy to store and transport.
Each package has labels and instructions, and the product is shipped to the customer and put into the market.
Step 7: Track and Record
Throughout the DIP production process, tracking and recording are critical.
The manufacturing process of each electronic component needs to be recorded in detail to trace problems and improve crafts.
We should record every production step, including the source of raw materials, manufacturing parameters, test results, and employee operation records.
These records can help DIP production track product quality and are a significant part of the quality management system.
Step 8: Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement in DIP production is the key to remaining competitive.
It includes optimizing production equipment, improving process flow, training employees to improve their skill levels, and adopting new technologies and materials.
Step 9: Environmental protection and sustainability
In the DIP production process, We try to reduce resource waste as much as possible, comply with environmental laws, ensure production sustainability, and obtain ISO and CE certification and RoHS compliance certification.
Summary
DIP production is a vital link in electronic component manufacturing, which requires multiple complex and precise steps to ensure the quality and performance of the final product.
From the raw materials plan to the final packaging and shipment requires expertise and strict quality control.
At the same time, we cannot ignore tracking, recording, continuous improvement, environmental protection, and sustainability. These help ensure the quality, efficiency, and sustainability of the production process.
In general, DIP production is a complex, multi-level process that includes product manufacturing, supply chain management, quality control, innovation, market expansion, and many other aspects.
Latest Blog
Table of Content
Contcat Us
Phone: +86-18123905375
Email: sales@circuitcardassembly.com
Skype: ali_youte
WhatsApp: +86-18123905375
Wechat: +86-18123905375










 Afrikaans
Afrikaans Shqip
Shqip አማርኛ
አማርኛ العربية
العربية Հայերեն
Հայերեն Azərbaycan dili
Azərbaycan dili Euskara
Euskara Беларуская мова
Беларуская мова বাংলা
বাংলা Bosanski
Bosanski Български
Български Català
Català Cebuano
Cebuano Chichewa
Chichewa 简体中文
简体中文 繁體中文
繁體中文 Corsu
Corsu Hrvatski
Hrvatski Čeština
Čeština Dansk
Dansk Nederlands
Nederlands Esperanto
Esperanto Eesti
Eesti Filipino
Filipino Suomi
Suomi Français
Français Frysk
Frysk Galego
Galego ქართული
ქართული Deutsch
Deutsch Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά ગુજરાતી
ગુજરાતી Kreyol ayisyen
Kreyol ayisyen Harshen Hausa
Harshen Hausa Ōlelo Hawaiʻi
Ōlelo Hawaiʻi עִבְרִית
עִבְרִית हिन्दी
हिन्दी Hmong
Hmong Magyar
Magyar Íslenska
Íslenska Igbo
Igbo Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia Gaeilge
Gaeilge Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 Basa Jawa
Basa Jawa ಕನ್ನಡ
ಕನ್ನಡ Қазақ тілі
Қазақ тілі ភាសាខ្មែរ
ភាសាខ្មែរ 한국어
한국어 كوردی
كوردی Кыргызча
Кыргызча ພາສາລາວ
ພາສາລາວ Latin
Latin Latviešu valoda
Latviešu valoda Lietuvių kalba
Lietuvių kalba Lëtzebuergesch
Lëtzebuergesch Македонски јазик
Македонски јазик Malagasy
Malagasy Bahasa Melayu
Bahasa Melayu മലയാളം
മലയാളം Maltese
Maltese Te Reo Māori
Te Reo Māori मराठी
मराठी Монгол
Монгол ဗမာစာ
ဗမာစာ नेपाली
नेपाली Norsk bokmål
Norsk bokmål پښتو
پښتو فارسی
فارسی Polski
Polski Português
Português ਪੰਜਾਬੀ
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ Română
Română Русский
Русский Samoan
Samoan Gàidhlig
Gàidhlig Српски језик
Српски језик Sesotho
Sesotho Shona
Shona سنڌي
سنڌي සිංහල
සිංහල Slovenčina
Slovenčina Slovenščina
Slovenščina Afsoomaali
Afsoomaali Español
Español Basa Sunda
Basa Sunda Kiswahili
Kiswahili Svenska
Svenska Тоҷикӣ
Тоҷикӣ தமிழ்
தமிழ் తెలుగు
తెలుగు ไทย
ไทย Türkçe
Türkçe Українська
Українська اردو
اردو O‘zbekcha
O‘zbekcha Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt Cymraeg
Cymraeg isiXhosa
isiXhosa יידיש
יידיש Yorùbá
Yorùbá Zulu
Zulu