What Is PCB Assembly? How to Assemble PCBs and Why It Matters for Electronics?
Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Assembly plays a essential part in the cutting edge hardware industry, serving as the spine for all electronic gadgets. This handle, regularly alluded to as PCB Assembly or PCBA, includes mounting electronic components onto a created PCB to make a utilitarian amassed circuit board. This direct investigates what PCB assembly involves, the steps to gather PCBs, and its basic significance in electronics.
Understanding PCB Assembly
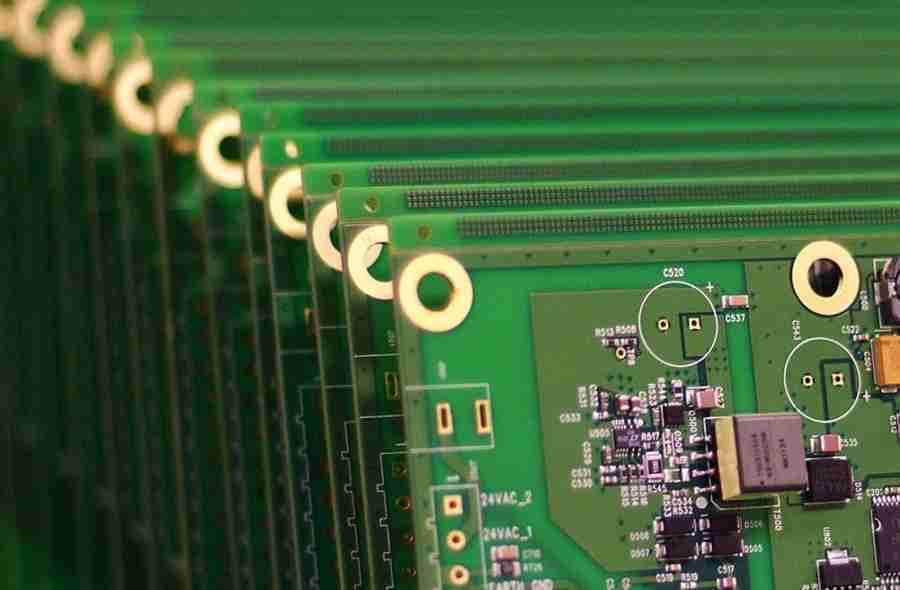
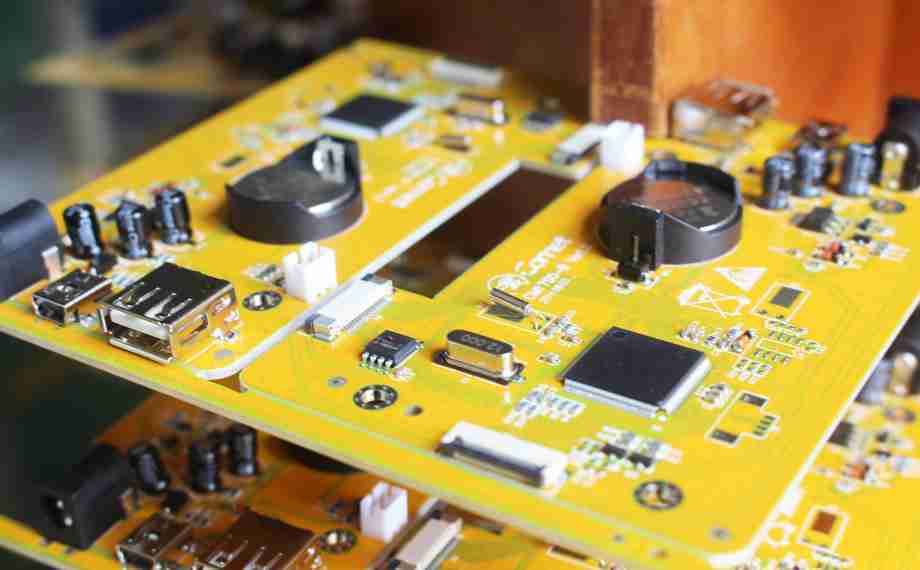
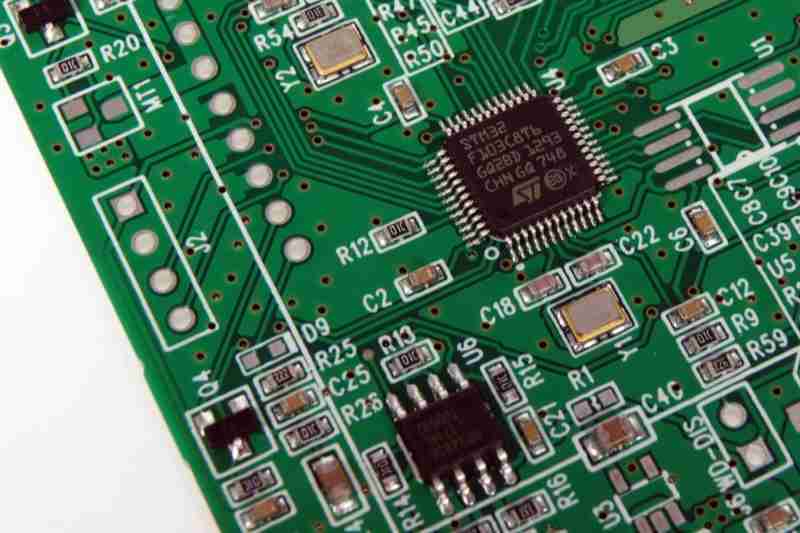
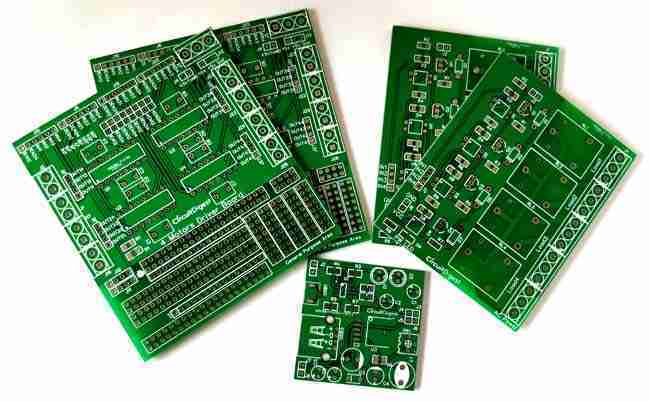
A Printed Circuit Board is a covered board composed of non-conductive substrate fabric, layered with copper follows that build up associations between electronic components. In any case, a PCB alone is not useful; it requires the assembly of electronic components to make a working gadget. This handle, named PCB Assembly, changes a uncovered PCB into an operational component of electronic devices.
PCB assembly can include either through-hole technology (THT), surface mount technology (SMT), or a combination of both. Each technology has particular applications and points of interest, making the choice subordinate on the plan and utilitarian necessities of the electronics.
The Process of Assembling PCBs
1. Planning of the PCB and Components
The assembly prepare starts with sourcing the components recorded in the bill of materials (BOM). These incorporate resistors, capacitors, diodes, microchips, and other electronic components. At the same time, the uncovered PCB is created to coordinate the plan details, guaranteeing the copper follows adjust with the expecting layout.
2. Solder Paste Application
For SMT-based PCB assembly, patch glue is connected to the surface of the PCB at focuses where components will be mounted. This glue, a blend of powdered patch and flux, holds the components in put incidentally some time recently soldering.
3. Component Placement
Automatic pick-and-place machines position the electronic components on the PCB. These machines are exceedingly exact, competent of setting components on perplexing plans inside milliseconds. For THT assembly, components are physically or robotically embedded into the penetrated holes.
4. Soldering Process
• Reflow Fastening (SMT): After component arrangement, the PCB is passed through a reflow broiler. Controlled warm dissolves the patch glue, making changeless electrical and mechanical connections.
• Wave Fastening (THT): For through-hole components, the PCB is passed over a wave of liquid patch, fastening all uncovered ranges and securing components to the board.
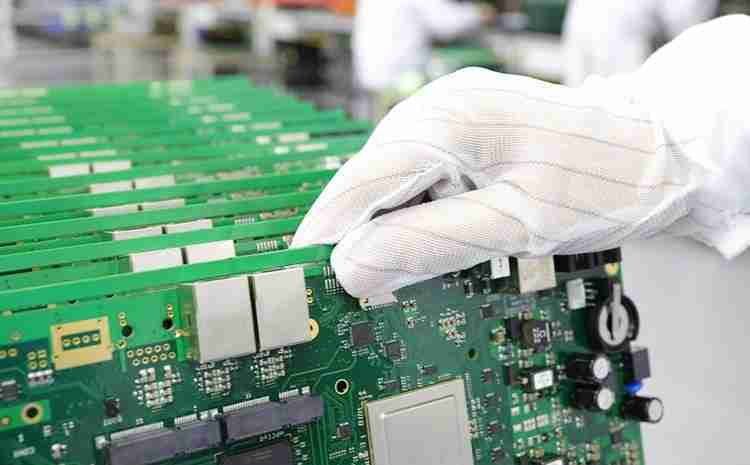
5. Inspection and Quality Control
Thorough assessment guarantees that the collected circuit board meets the required determinations. Strategies such as optical inspection (AOI), X-ray assessment, and utilitarian testing offer assistance recognize any deficiencies or misplacements.
6. Final Assembly and Testing
Once the components are patched and reviewed, the PCB experiences last assembly. Extra parts, like connectors and chassis, may be included. Testing guarantees the completed PCB capacities as expecting, assembly quality and execution standards.
Why PCB Assembly Things for Electronics
1. Empowers Compact Design
Modern hardware request compactness and usefulness. PCB assembly permits originators to make perplexing circuits on negligible space, coordination different functionalities into a little impression. Methods like SMT diminish the measure of components, making it conceivable to create lightweight and versatile devices.
2. Guarantees Unwavering quality and Performance
A legitimately collected PCB ensures steady associations and vigorous execution. Progressed fastening strategies guarantee components remain safely in put, indeed beneath mechanical push or tall temperatures, improving the life span of electronic devices.
3. Speeds Up Production
Automation in PCB assembly, counting pick-and-place machines and reflow fastening stoves, drastically increments generation speed. This is pivotal for businesses like customer hardware and broadcast communications, where request for unused items is constant.
4. Diminishes Costs
Efficient PCB Assembly brings down generation costs by minimizing blunders, diminishing fabric wastage, and expanding throughput. The prepare moreover underpins adaptability, permitting producers to meet request without over the top expenditure.
5. Fundamental for Innovative Advancements
PCBs are the establishment of advancement in businesses extending from healthcare to aviation. High-quality amassed circuit sheets are irreplaceable in creating cutting-edge advances like IoT gadgets, restorative hardware, and space investigation tools.
Types of PCB Assembly
1. Single-Sided Assembly
Single-sided PCB Assembly includes putting components on one side of the board. This sort is cost-effective and suited for basic gadgets like calculators and Driven lighting systems.
2. Double-Sided Assembly
Here, components are mounted on both sides of the PCB, empowering more complex circuitry in a littler impression. It’s commonly utilized in domestic machines and communication devices.
3. Multi-Layer Assembly
Multi-layer PCB Assembly joins numerous layers of circuitry, frequently sandwiched together. These PCBs are perfect for high-speed gadgets, servers, and progressed computing frameworks where space optimization and flag astuteness are critical.
Challenges in PCB Assembly
1. Miniaturization
As gadgets gotten to be littler, the measure of components and follow dividing on PCBs moreover decreases, making assembly profoundly challenging. Exactness devices and progressed procedures are fundamental to meet these demands.
2. Thermal Management
Heat scattering is basic in high-power gadgets. Destitute warm administration amid PCB Assembly can lead to overheating, component harm, and decreased gadget lifespan.
3. Quality Assurance
Even minor deficiencies, such as a single unsoldered association, can render a PCB out of commission. Hence, keeping up tall guidelines of quality control is non-negotiable.
Innovations in PCB Assembly
1. Progressed Materials
Innovative materials like adaptable PCBs and high-frequency substrates are growing the conceivable outcomes of electronic plan. These materials require specialized Assembly forms to handle their special characteristics.
2. Machine Learning and AI
AI and machine learning are upgrading assessment and quality control. These advances move forward imperfection discovery precision and decrease time-consuming manual reviews.
3. 3D Printing
3D printing in PCB assembly permits for quick prototyping and the improvement of complicated board plans, quickening item improvement timelines.
Best Practices for Assembling PCBs
• Select the Right Producer: Accomplice with an experienced PCB Assembly supplier who gets it your plan necessities and application needs.
• Optimize Design for Manufacturability (DFM): Guarantee the PCB format is outlined to encourage simple and cost-effective assembly.
• Perform Thorough Testing: Numerous levels of testing—from in-circuit to functional—can reveal potential issues early in the generation cycle.
• Invest in Training and Technology: Keeping up with industry progressions guarantees that the Assembly handle meets current requests and future-proof standards.
Conclusion
PCB Assembly is a foundation of the gadgets industry, giving the implies to change uncovered circuit sheets into useful components. From empowering the miniaturization of gadgets to guaranteeing unwavering quality and cost-efficiency, the handle is central to innovative advance. By understanding how to amass PCBs and why they matter, producers and engineers can thrust the boundaries of development, creating groundbreaking electronic arrangements for an interconnected world. The advancement of gathered circuit board forms proceeds to clear the way for more brilliant, more productive, and flexible gadgets.
Latest Blog
Table of Content
Contcat Us
Phone: +86-18123905375
Email: sales@circuitcardassembly.com
Skype: ali_youte
WhatsApp: +86-18123905375
Wechat: +86-18123905375










 Afrikaans
Afrikaans Shqip
Shqip አማርኛ
አማርኛ العربية
العربية Հայերեն
Հայերեն Azərbaycan dili
Azərbaycan dili Euskara
Euskara Беларуская мова
Беларуская мова বাংলা
বাংলা Bosanski
Bosanski Български
Български Català
Català Cebuano
Cebuano Chichewa
Chichewa 简体中文
简体中文 繁體中文
繁體中文 Corsu
Corsu Hrvatski
Hrvatski Čeština
Čeština Dansk
Dansk Nederlands
Nederlands Esperanto
Esperanto Eesti
Eesti Filipino
Filipino Suomi
Suomi Français
Français Frysk
Frysk Galego
Galego ქართული
ქართული Deutsch
Deutsch Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά ગુજરાતી
ગુજરાતી Kreyol ayisyen
Kreyol ayisyen Harshen Hausa
Harshen Hausa Ōlelo Hawaiʻi
Ōlelo Hawaiʻi עִבְרִית
עִבְרִית हिन्दी
हिन्दी Hmong
Hmong Magyar
Magyar Íslenska
Íslenska Igbo
Igbo Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia Gaeilge
Gaeilge Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 Basa Jawa
Basa Jawa ಕನ್ನಡ
ಕನ್ನಡ Қазақ тілі
Қазақ тілі ភាសាខ្មែរ
ភាសាខ្មែរ 한국어
한국어 كوردی
كوردی Кыргызча
Кыргызча ພາສາລາວ
ພາສາລາວ Latin
Latin Latviešu valoda
Latviešu valoda Lietuvių kalba
Lietuvių kalba Lëtzebuergesch
Lëtzebuergesch Македонски јазик
Македонски јазик Malagasy
Malagasy Bahasa Melayu
Bahasa Melayu മലയാളം
മലയാളം Maltese
Maltese Te Reo Māori
Te Reo Māori मराठी
मराठी Монгол
Монгол ဗမာစာ
ဗမာစာ नेपाली
नेपाली Norsk bokmål
Norsk bokmål پښتو
پښتو فارسی
فارسی Polski
Polski Português
Português ਪੰਜਾਬੀ
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ Română
Română Русский
Русский Samoan
Samoan Gàidhlig
Gàidhlig Српски језик
Српски језик Sesotho
Sesotho Shona
Shona سنڌي
سنڌي සිංහල
සිංහල Slovenčina
Slovenčina Slovenščina
Slovenščina Afsoomaali
Afsoomaali Español
Español Basa Sunda
Basa Sunda Kiswahili
Kiswahili Svenska
Svenska Тоҷикӣ
Тоҷикӣ தமிழ்
தமிழ் తెలుగు
తెలుగు ไทย
ไทย Türkçe
Türkçe Українська
Українська اردو
اردو O‘zbekcha
O‘zbekcha Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt Cymraeg
Cymraeg isiXhosa
isiXhosa יידיש
יידיש Yorùbá
Yorùbá Zulu
Zulu