The printed circuit board( PCB) market has experienced significant elaboration over the once many decades, and the cast period between 2025 and 2030 is poised to witness unknown growth. The adding relinquishment of advanced electronic devices, rapid-fire artificial automation, and technological improvements in areas similar as 5G, artificial intelligence( AI), and electric vehicles( EVs) are driving this market’s expansion. This composition explores the PCB market’s size, assiduity dynamics, crucial trends, and growth factors anticipated to shape the geography between 2025 and 2030.
Overview of the printed Circuit Board market
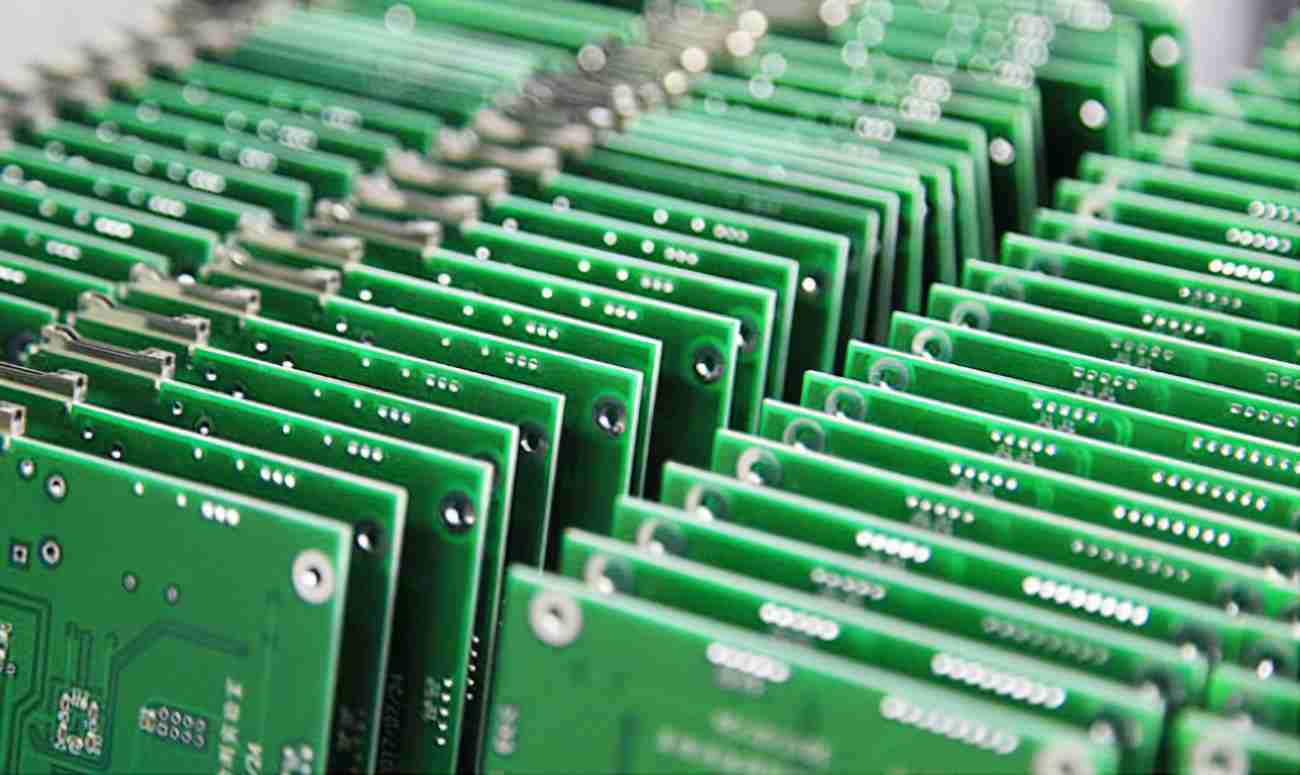
Printed circuit boards are a foundational element of nearly every electronic device. They serve as the mechanical and electrical backbone, connecting and supporting electronic factors like capacitors, resistors, and transistors. Available in colourful types, including single- sided, double-sided, multi-layered, and high-density interconnect (HDI) PCBs, they feed to different diligence ranging from consumer electronics to aerospace.
Market Size and Growth Projections
The global PCB market, valued at roughly USD 72 billion in 2024, is projected to reach over USD 110 billion by 2030, growing at a compound annual growth rate( CAGR) of 7.5 during the cast period. This growth can be attributed to the following factors
1. Expansion of Consumer Electronics
The global proliferation of smart phones, tablets, laptops, and wearable’s has created a sustained demand for PCBs. Inventions like foldable screens and compact device designs are farther driving the market.
2. 5G Technology Rollout
The deployment of 5G networks worldwide requires sophisticated PCBs with advanced signal integrity and frequency operation. This demand is a major growth motorist multi-layer and HDI PCBs.
3. Automotive Electrification
The rise of EVs and independent vehicles is transubstantiating the automotive assiduity, leading to increased demand for advanced PCBs for battery operation, charging systems, and in- vehicle communication networks.
4. Industrial Automation and IoT
The relinquishment of smart manufacturing and IoT devices necessitates PCBs that support miniaturization, reliability, and high performance in rugged surroundings.
5. Healthcare Advancements
The medical device assiduity is decreasingly counting on miniaturized and flexible PCBs for operations similar as wearable health observers, implantable devices, and individual outfit.
Key Market Segments
The PCB market is segmented by type, substrate, end- stoner assiduity, and region.
1. By Type
• Single-Sided PCBs: Generally used in low- complexity devices due to their simple design.
• Double-Sided PCBs: Set up in mid-range devices taking further complexity.
• Multi-Layer PCBs: Essential for high- performance operations in aerospace, defense, and data centers.
• HDI PCBs: Preferred for compact, high- speed devices like smart phones and IoT widgets.
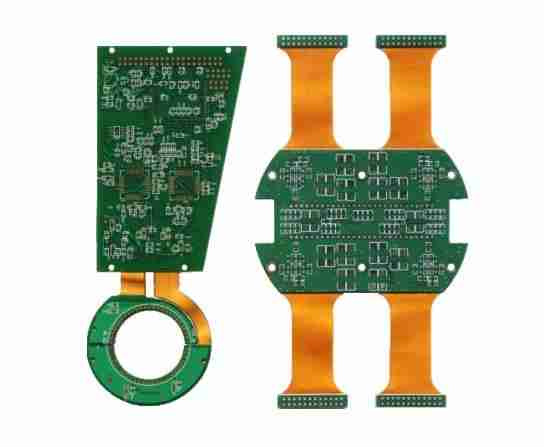
• Rigid and Flexible PCBs: Serving diligence with specific design conditions, similar as automotive and healthcare.
2. By Substrate
• Rigid Substrate PCBs: Used in durable electronics like computers and artificial machines.
• Flexible Substrate PCBs: Suitable for wearable devices and foldable electronics.
• Rigid-Flex PCBs: Combining the strengths of both types for operations like aerospace and robotics.
3. By End-stoner Assiduity
• Consumer Electronics: Smartphone, tablets, and wearable.
• Automotive: EVs, advanced motorist backing systems( ADAS), and infotainment systems.
• Healthcare: Implantable devices and individual tools.
• Industrial Automation: IoT devices and robotics.
• Telecommunications: 5G structure and networking devices.
• Aerospace and Defense: Radar systems, avionics, and military- grade electronics.
Regional Analysis Market Dynamics Across Key Geographies
The PCB market’s growth is not invariant encyclopaedically, as each region exhibits unique motorists and challenges. Understanding indigenous market dynamics is essential for stakeholders aiming to maximize openings.
1. Asia- Pacific( APAC)
Market Share and Growth: APAC remains the dominant player, counting for over 50 of global PCB product. China, Taiwan, South Korea, and Japan are crucial contributors.
Drivers
• A well- established electronics manufacturing ecosystem.
• Rapid advancements in EV product, particularly in China.
• High demand for consumer electronics and artificial automation equipment.
Challenges
• Environmental enterprises related to manufacturing processes.
• adding labour costs in some regions.
2. North America
Market Share and Growth: North America represents a significant share of the PCB market, driven by invention and high- value operations.
Drivers
• Strong demand for PCBs in aerospace, defence, and healthcare.
• The growing relinquishment of IoT and AI- grounded systems.
Challenges
• Dependence on significances for low- cost PCB product.
• Compliance with strict environmental and safety regulations.
3. Europe
Market Share and Growth: Europe is witnessing steady growth, supported by advancements in automotive and artificial sectors.
Drivers
• Electrification of the automotive assiduity, particularly in Germany.
• Investments in renewable energy and artificial robotization.
Challenges
• force chain dislocations due to geopolitical pressures.
• High product costs compared to APAC.
4. Rest of the World
Market Share and Growth: Arising markets in South America, Africa, and the Middle East are gradationally contributing to PCB demand.
Drivers
• Adding investments in structure and telecommunications.
• Growing consumer electronics market.
Challenges
• Limited access to advanced manufacturing technology.
• profitable and political insecurity in some regions.
Key Trends Driving the PCB Market
1. Miniaturization of devices
As electronic devices come lower and more sophisticated, the need for compact PCBs with advanced element viscosity is rising. HDI PCBs and multi-layer designs are addressing these conditions.
2. Flexible Electronics
Flexible and rigid-flex PCBs are gaining traction due to their capability to acclimatize to unconventional shapes and reduce assembly weight, critical for diligence like automotive and aerospace.
3. Sustainability and Green Manufacturing
With environmental enterprises gaining elevation, PCB manufacturers are espousing eco-friendly practices, similar as lead-free soldering and biodegradable substrates.
4. Advancements in Substrate Accoutrements
The development of advanced accoutrements , similar as high- frequency laminates and ceramic- grounded substrates, enhances PCBs’ performance in demanding operations like 5G and radar systems.
5. Emergence of Assiduity 4.0
Automation and digitalization in manufacturing are driving the demand for smart PCBs that can affiliate seamlessly with IoT and AI- driven systems.
6. Increased Outsourcing
Many companies are outsourcing PCB product to regions with cost-effective manufacturing, particularly in APAC, to remain competitive.
Challenges in the PCB market
Despite promising growth, the PCB assiduity faces several challenges
1. Raw Material force
Fluctuations in raw material prices, similar as bobby and laminates, can impact product costs and profit perimeters.
2. Environmental Regulations
Strict regulations regarding electronic waste disposal and dangerous substances bear investments in sustainable practices, which can increase product costs.
3. Technological Complexity
Designing and manufacturing high- performance PCBs for advanced operations bear significant moxie and R&D investments.
4. Global force Chain dislocations
Geopolitical pressures and trade restrictions can disrupt the force chain, affecting the vacuity of factors and raw accoutrements .
Future Outlook
The PCB market’s future between 2025 and 2030 looks promising, driven by technological advancements and expanding operations across diligence. crucial openings include
1. Integration with Emerging Technologies
The development of PCBs acclimatized for AI, machine literacy, and stoked reality operations.
2. Growth in Renewable Energy
The renewable energy sector, including solar panels and wind turbines, will drive demand for durable and effective PCBs.
3. Customization and Prototyping
Increased focus on customized PCB designs and rapid-fire prototyping to meet unique assiduity conditions.
4. Focus on Circular Economy
Relinquishment of recycling and exercise practices to minimize environmental impact and misbehave with strict regulations.
5. Healthcare inventions
The medical device assiduity’s reliance on PCBs for perfection and trust ability will continue to grow.
The part of PCB Manufacturers in Driving market Growth
As the PCB market evolves, manufacturers are playing a critical part in shaping the assiduity’s line. Through strategic investments in technology, sustainability, and invention, they’re addressing current demands while preparing for unborn challenges. crucial areas of focus for manufacturers include
1. Investments in Research and Development
Leading PCB manufacturers are prioritizing R&D to develop advanced products, similar as HDI PCBs, rigid- flex boards, and multi-layer designs.
Concentrated invention enables manufacturers to feed to the growing demand for compact, effective, and high- performance boards in operations like 5G, EVs, and medical devices.
2. Relinquishment of Smart Manufacturing Practices
Assiduity 4.0 technologies, including robotics, artificial intelligence, and machine literacy, are transubstantiating PCB manufacturing.
Smart manufactories enable manufacturers to streamline product processes, reduce waste, and achieve advanced perfection, meeting the strict quality conditions of sectors like aerospace and defense.
3. Collaboration with End- druggies
Close collaboration between PCB manufacturers and their guests ensures the development of customized results acclimatized to specific requirements, similar as automotive- grade PCBs or ultra-flexible designs for wearables.
Prototyping and feedback circles enhance product design and functionality, fostering long- term partnerships.
4. Commitment to Sustainability
Eco-friendly practices, similar as using recyclable accoutrements and minimizing dangerous substances, are getting a standard in PCB manufacturing.
Companies that borrow sustainable styles gain a competitive edge, as environmental compliance becomes decreasingly pivotal in global markets.
Emerging Applications and Future Trends
As technology evolves, new operations for PCBs are arising, creating openings for growth and invention. crucial unborn trends include
1. PCBs for Quantum Computing
The development of amount computers requires ultra-high perfection PCBs to handle delicate amount processors.
Specialized PCBs with advanced accoutrements and ultra-low noise characteristics are getting critical for this frontier technology.
2. Renewable Energy results
PCBs are essential in renewable energy systems, similar as solar inverters, wind turbine regulators, and battery operation systems.
As global sweats to combat climate change consolidate, the demand for durable and effective PCBs in this sector will rise.
3. Space Exploration and Satellites
The adding deployment of satellites and growth in marketable space disquisition demand high- trust ability PCBs that can operate under extreme conditions.
Innovations in thermal operation and radiation resistance are pivotal for these operations.
4. Advanced motorist Assistance Systems( ADAS)
Autonomous vehicles calculate heavily on ADAS, which requires sophisticated PCBs for real- time data processing and communication.
The drive toward full vehicle autonomy will further accelerate demand for high- performance automotive PCBs.
5. Wearable Technology
The wearable device market, including fitness trackers, smart spectacles, and health observers, continues to grow.
Flexible and ultra-thin PCBs are essential for creating comfortable and effective wearable.
Opportunities for Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
While large pots dominate the PCB market, SMEs have significant openings to sculpt out niches. Strategies for success include:
1. Niche Market Focus
SMEs can target technical operations, similar as custom PCBs for medical devices or low- volume product for prototyping.
By focusing on specific diligence, lower companies can separate themselves from larger challengers.
2. Technology Partnerships
Collaborating with technology providers and exploration institutions can help SMEs access advanced manufacturing ways and accoutrements .
3. Export openings
SMEs in cost-effective manufacturing regions can subsidize on import openings, feeding to markets in North America and Europe.
4. Emphasis on Quality
Building a character for high- quality products and reliability can lead to long- term customer connections.
Conclusion
The printed circuit board market is set to witness remarkable growth from 2025 to 2030, fueled by advancements in technology and expanding operations across diligence. With demand surging in sectors like consumer electronics, automotive electrification, healthcare, and telecommunications, the PCB industry is entering a golden period of invention and expansion.
While challenges similar as environmental compliance, force chain dislocations, and technological complexity persist, the assiduity’s adaptability and rigidity position it for long- term success. crucial trends like miniaturization, flexible electronics, and green manufacturing are shaping the market’s future, ensuring its applicability in a fleetly changing technological geography.
Stakeholders, including manufacturers, suppliers, and end- druggies, have immense openings to influence the PCB market’s growth. By espousing innovative technologies, fastening on sustainability, and feeding to arising operations, the assiduity is poised to play a central part in the global electronics ecosystem for times to come.