What Is the Difference Between PCBA and PCB?
In electronic devices, the terms “PCB” and “PCBA” are much used, frequently traded but they actually represent different stages in the production of electronic circuit boards. A PCB, or Printed Circuit Board, and a PCBA, or Printed Circuit Board Assembly, are two very important things for electronic devices, but they play very specific roles and have different statuses at different steps of the production cycle. Understanding the contrasts between them is imperative in the field of hardware fabricating, as each has interesting qualities, applications, and fabricating forms. Let’s investigate what isolates these two basic components of gadgets, counting their definitions, characteristics, and the forms included in making them.
Understanding PCBs
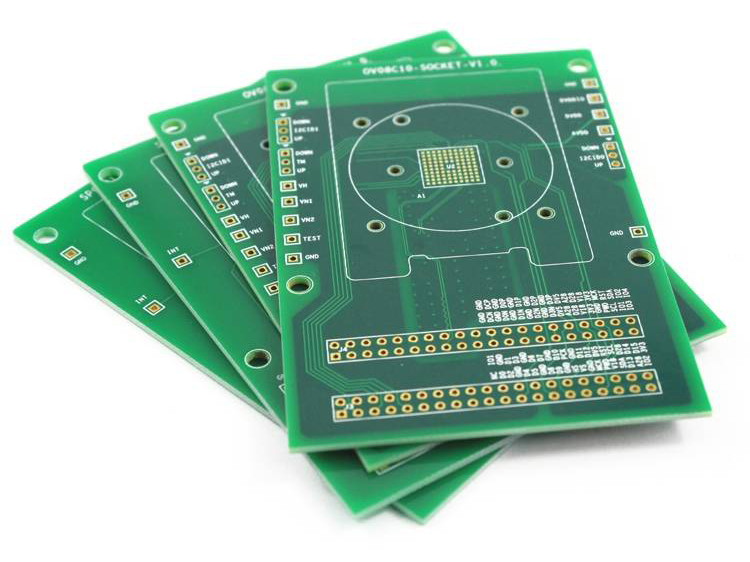
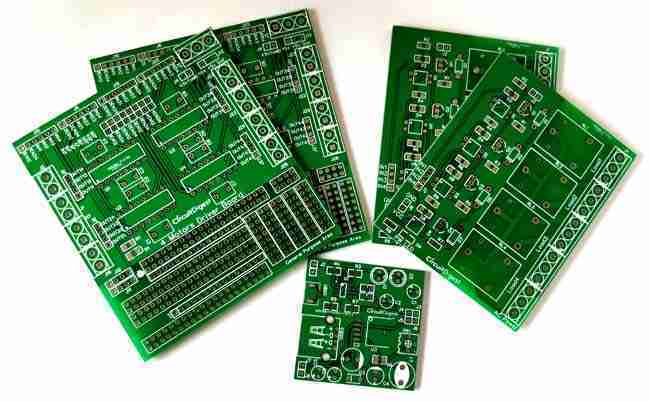
A printed circuit board is essentially a standard component of electronic devices that provides the physical structure to support and connect electronic components. In its least complex frame, a PCB is a level, frequently green board made of non-conductive fabric, ordinarily fibreglass, epoxy, or other composite materials, on which a lean layer of conductive fabric (as a rule copper) is covered. This copper layer is carved with pathways, known as follows, which permit for electrical associations between diverse components when assembled.
Types of PCBs
PCBs shift in complexity and setup, with the essential sorts being:
1. Single-layer PCBs: The most elementary type, consisting of a single layer of conductive copper, which is used in simple electronics such as calculators and radios.
2. Double-layer PCBs: In these, conductive layers are provided on both sides of the board, thereby giving extra space for circuitry. They are frequently utilized in more complex gadgets, such as mechanical controls.
3. Multi-layer PCBs: Comprising of three or more layers, these are utilized in advanced hardware like shrewd phones, computers, and restorative equipment.
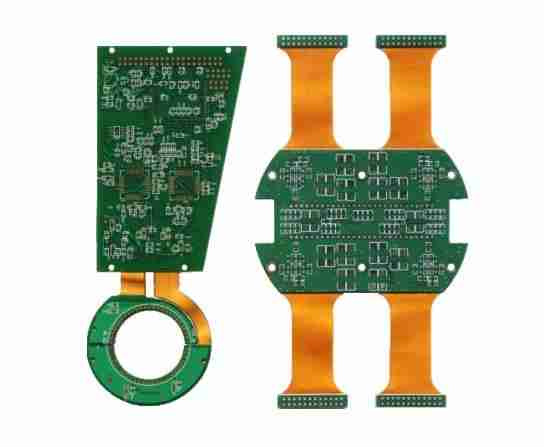
4. Rigid, Flex, and Rigid-Flex PCBs: These varieties are based on adaptability needs. Unbending PCBs are most common and resolute, whereas flex and rigid-flex sorts permit for more plan flexibility in tight spaces, as they can twist or fold.
Key Functions of a PCB
The PCB plays a vital part in electronic gadgets, satisfying a few functions:
1. Structural support: The PCB physically underpins different components, counting resistors, capacitors, and ICs (integrated circuits), keeping them solidly in place.
2. Electrical pathways: The copper follows act as a guide for electric signals, empowering components to communicate.
3. Heat dissipation: PCBs can incorporate layers and components that offer assistance scatter warm from high-power applications, progressing gadget longevity.
4. Signal routing: In complex multi-layer PCBs, flag judgment is significant, especially in high-frequency gadgets where any obstructions can prevent performance.
PCB Design and Manufacturing
The prepare of making a PCB includes a few perplexing steps, ordinarily beginning with the plan stage, taken after by manufacturing.
1. Design: Engineers utilize PCB plan computer program to make a outline, carefully arranging the situation of follows, cushions, vias, and components.
2. Printing the format: Once the plan is affirmed, it is printed onto a fabric, ordinarily a photo stand up to, which will offer assistance direct the carving process.
3. Etching: The copper-clad board is carved to evacuate pointless copper, taking off as it were the wanted circuitry pattern.
4. Drilling and plating: For multi-layer PCBs, gaps are bored for vias (interconnects between layers), and these are plated with conductive materials to guarantee continuity.
5. Solder mask and silk-screening: A patch veil is connected to avoid inadvertent fastening on unintended ranges, and a silkscreen is included to name the board with portion numbers, images, and logos.
Applications of PCBs
Due to their flexibility, PCBs are found in about all advanced electronic gadgets, counting buyer gadgets, restorative gear, car hardware, mechanical apparatus, and more.
Understanding PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly)
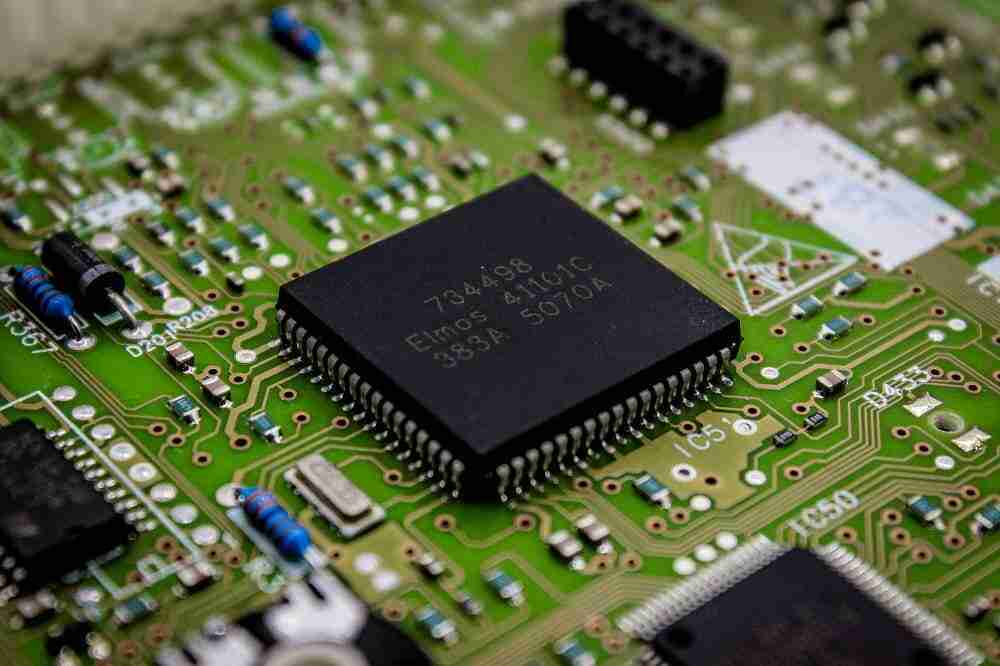
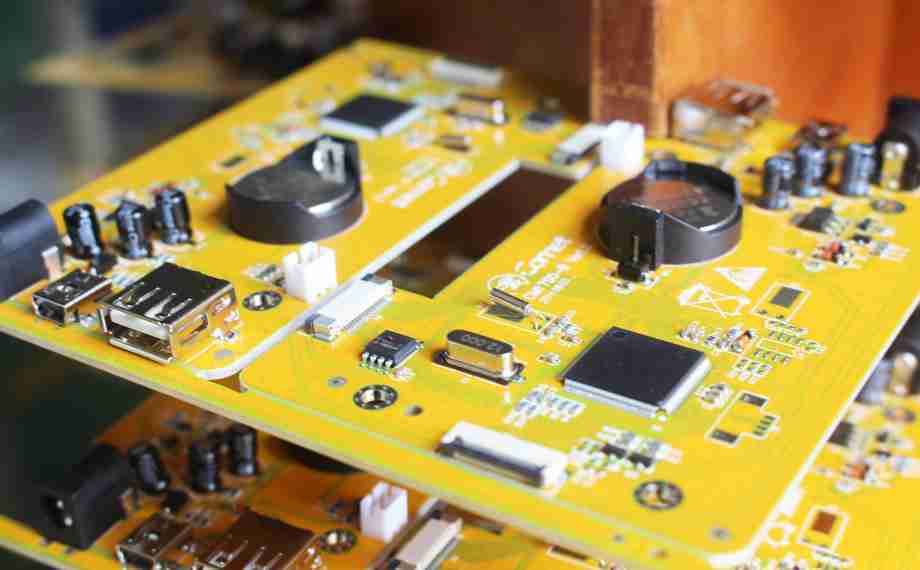
Once a PCB is made, it is prepared to enter the Assembly stage, where it gets to be a Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA). A PCBA is basically a PCB that has been populated with all essential electronic components, changing it into a useful portion of an electronic device.
PCBA Assembly Process
The Assembly handle includes a few steps and depends on both computerization and manual techniques:
1. Solder paste application: A stencil is utilized to apply patch paste to particular regions on the board where components will be set. The paste contains a blend of flux and little balls of patch that will inevitably intertwine the components to the PCB.
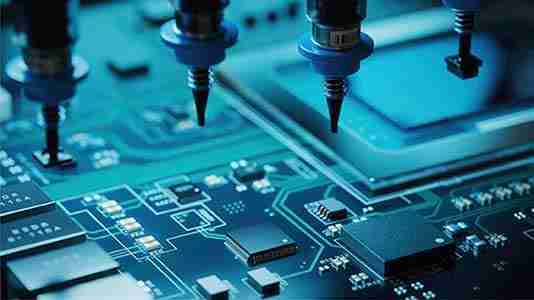
2. Pick and put: Robotized pick-and-place machines position electronic components on the board in their assigned spots, agreeing to the PCB plan. These machines are exceedingly precise and can put hundreds of components per minute.
3. Soldering: After putting components, the board goes through a reflow broiler where the patch paste softens and makes a solid electrical and mechanical bond between components and the PCB. For double-sided congregations, both sides may experience reflow.
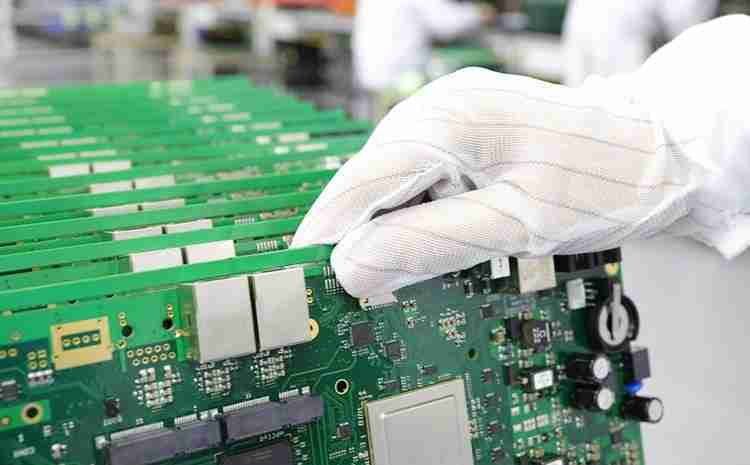
4. Inspection and testing: The gathered PCB experiences thorough reviews and tests, such as automated optical inspection (AOI), X-ray review, and useful testing to guarantee there are no absconds like shorts, opens, or erroneous placements.
5. Through-hole soldering: For components that require more grounded mechanical bonds or cannot withstand reflow warm, through-hole patching is utilized. Components are set in penetrated gaps and fastened either physically or with wave soldering.
6. Cleaning and coating: To avoid contaminants from influencing the PCB’s execution, a few PCBAs experience a cleaning handle. A conformal coating may too be connected for extra security, particularly in unforgiving environments.
Differences in Types of PCBAs
Just as PCBs come in different arrangements, so do PCBAs. They can be single-sided, double-sided, or multi-layered, depending on the complexity of the plan and the application. Also, PCBAs may incorporate particular components or methods custom-made for a specific environment or execution standard.
Differences Between PCB and PCBA
Although closely related, PCBs and PCBAs serve distinctive purposes and speak to unmistakable stages in hardware generation. Here are a few of the essential differences:
1. Definition and Purpose:
• A PCB is a uncovered board that as it were has the circuitry carved into it, without any electronic components.
• A PCBA is a PCB that has been amassed with components, making it prepared for establishment in an electronic device.
2. Manufacturing Process:
• The fabricating handle for a PCB includes planning and carving conductive pathways on a substrate.
• PCBA fabricating includes joining electronic components onto a PCB through patching, review, and testing.
3. Functionality:
• A PCB by itself is not useful; it as it were acts as a stage for future components.
• A PCBA, on the other hand, is utilitarian and can be tried and coordinates into bigger electronic systems.
4. Appearance:
• A PCB is more often than not level and as it were contains conductive follows without any components.
• A PCBA incorporates components such as resistors, capacitors, ICs, and other electronic parts, making it show up more complex and bulky.
5. Cost Differences:
• PCBs are for the most part less costly to deliver than PCBAs, as they don’t incorporate components or Assembly labour.
• PCBAs are more exorbitant due to the included taken a toll of components, labor for Assembly, and quality inspection.
6. Applications:
• PCBs are utilized as the base or skeleton of electronic circuits and can be utilized by themselves for testing and prototyping.
• PCBAs are utilized in the last Assembly of electronic items where they work as the central working circuitry of devices.
PCB vs. PCBA: Which One Do You Need?
For a producer, whether to arrange a PCB or a PCBA depends on the arrange of generation. Here’s how to decide:
• Prototyping: Amid prototyping, engineers may begin with clear PCBs to test different formats some time recently contributing in components and assembly.
• Mass Generation: For full-scale generation, companies ordinarily arrange PCBAs since they are completely gathered and prepared for establishment in last products.
Advancements in PCB and PCBA Technology
Both PCB and PCBA innovations are continually advancing, with advancements pointed at decreasing estimate, expanding usefulness, and moving forward unwavering quality. A few of the most recent headways include:
1. HDI PCBs: High-Density Interconnect (HDI) innovation permits more circuits to fit in littler ranges, perfect for compact gadgets like shrewd phones.
2. Flexible and Rigid-Flex PCBAs: Adaptable PCBAs permit gadgets to withstand development and bowing, making them basic for wearable hardware and therapeutic devices.
3. Advanced Testing Procedures: Developments in assessment and testing, like AOI and X-ray, offer assistance guarantee PCBA quality, particularly as circuit plans gotten to be more intricate.
4. Automated Assembly: Mechanized Assembly procedures, like pick-and-place and reflow fastening, have essentially expanded the speed and precision of PCBA generation, lessening human mistake and costs.
5. 3D Printing for PCBs: In spite of the fact that still rising, 3D printing for PCBs has potential for quick prototyping, permitting for quicker plan iterations.
Importance of Quality Control in PCB and PCBA Manufacturing
Quality control is one of the most basic components in both PCB and PCBA fabricating, as the unwavering quality of the last electronic item intensely depends on these forms. Absconds in either the PCB or PCBA can lead to disappointments that affect the execution and security of the conclusion gadget. Here are a few key regions where quality control is essential:
1. Material Quality: For PCBs, the quality of the substrate fabric, like fibreglass or polyimide, and the copper utilized for follows plays a critical part in the strength and usefulness of the board. High-quality materials are fundamental, particularly for PCBs that must withstand tall temperatures or cruel natural conditions.
2. Precision in PCB Plan and Carving: Accuracy is essential to guarantee that follows are precisely set and do not cause shorts or obstructions. Amid carving, any blunder can lead to network issues. Subsequently, progressed machines and apparatuses are utilized to keep up tall accuracy in follow situation and size.
3. Component Quality in PCBA: The components utilized in a PCBA, such as resistors, capacitors, and ICs, must meet rigid benchmarks for life span and execution. Flawed or low-grade components can lead to gadget breakdown or early wear-out.
4. Assembly Exactness: Fastening mistakes, misaligned components, or inadequate associations can make issues in the PCBA, making useful testing basic. Robotized machines offer assistance decrease mistakes in high-precision Assembly, but manual review is regularly conducted to capture abandons that may go unnoticed by machines.
5. Testing Conventions: Each PCBA experiences testing conventions like Automated Optical Inspection (AOI), X-ray testing (for multi-layer boards where covered up associations require examination), and in-circuit or utilitarian testing to guarantee that it works as anticipated beneath different conditions.
Common Challenges in PCB and PCBA Production
The fabricating of PCBs and PCBAs is not without its challenges. As innovation propels, the request for littler, more complex boards presents one of a kind obstacles that producers must overcome.
Miniaturization and Complexity
With the thrust towards littler, more compact gadgets, particularly in the shopper gadgets industry, PCBs and PCBAs must fit more usefulness into restricted space. High-Density Interconnect (HDI) boards are an illustration of this, empowering more components on a littler impression. Be that as it may, this requires progressed gear and talented labor, expanding both taken a toll and complexity.
Thermal Management
As gadgets gotten to be more effective, they require for viable warm administration inside PCBs and PCBAs gets to be pivotal. Components that create a part of warm must be put deliberately, and materials that progress warm scattering, such as metal-core PCBs, are regularly utilized. Producers moreover have to consider warm sinks, warm vias, and other strategies to oversee and disseminate warm effectively.
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
As electronic gadgets increment in control and recurrence, they ended up more vulnerable to Electromagnetic Obstructions (EMI), which can disturb usefulness. In multi-layer PCBs and PCBAs, EMI control is fundamental, particularly for applications like remote gadgets and radio-frequency (RF) components. Methods such as establishing, protecting, and cautious follow steering are fundamental to decrease EMI.
Cost Considerations
PCBs and PCBAs with higher complexity require more assets, counting specialized apparatus, exceedingly gifted specialists, and now and then more costly materials. Overseeing costs whereas keeping up quality can be a challenge, particularly for littler companies or amid prototyping stages when the board plan might experience a few iterations.
Supply Chain and Component Availability
The gadgets industry regularly faces challenges in keeping up a steady supply chain. Deficiencies in components, such as semiconductors, can lead to delays in PCBA generation and expanded costs. Producers require to work closely with providers to guarantee the accessibility of high-quality components and adjust their generation plans to potential disturbances.
Conclusion
In summary, the primary difference between a PCB and a PCBA lies in their stage within the manufacturing process. A PCB is a bare, non-functional board that serves as the base structure for electronic circuits, while a PCBA is a fully assembled board, containing all necessary components to make it operational. Understanding the difference is essential for anyone involved in electronics manufacturing or design, as each component plays a critical role in the functionality of modern electronic devices.
With the rapid advancements in technology, both PCB and PCBA manufacturing processes are continually evolving, paving the way for smaller, more efficient, and more powerful electronic devices. Whether it’s for consumer electronics, medical devices, automotive systems, or industrial machinery, PCB and PCBA technologies remain at the heart of modern electronics, shaping the future of innovation.
Latest Blog
Table of Content
Contcat Us
Phone: +86-18123905375
Email: sales@circuitcardassembly.com
Skype: ali_youte
WhatsApp: +86-18123905375
Wechat: +86-18123905375

























 Afrikaans
Afrikaans Shqip
Shqip አማርኛ
አማርኛ العربية
العربية Հայերեն
Հայերեն Azərbaycan dili
Azərbaycan dili Euskara
Euskara Беларуская мова
Беларуская мова বাংলা
বাংলা Bosanski
Bosanski Български
Български Català
Català Cebuano
Cebuano Chichewa
Chichewa 简体中文
简体中文 繁體中文
繁體中文 Corsu
Corsu Hrvatski
Hrvatski Čeština
Čeština Dansk
Dansk Nederlands
Nederlands Esperanto
Esperanto Eesti
Eesti Filipino
Filipino Suomi
Suomi Français
Français Frysk
Frysk Galego
Galego ქართული
ქართული Deutsch
Deutsch Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά ગુજરાતી
ગુજરાતી Kreyol ayisyen
Kreyol ayisyen Harshen Hausa
Harshen Hausa Ōlelo Hawaiʻi
Ōlelo Hawaiʻi עִבְרִית
עִבְרִית हिन्दी
हिन्दी Hmong
Hmong Magyar
Magyar Íslenska
Íslenska Igbo
Igbo Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia Gaeilge
Gaeilge Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 Basa Jawa
Basa Jawa ಕನ್ನಡ
ಕನ್ನಡ Қазақ тілі
Қазақ тілі ភាសាខ្មែរ
ភាសាខ្មែរ 한국어
한국어 كوردی
كوردی Кыргызча
Кыргызча ພາສາລາວ
ພາສາລາວ Latin
Latin Latviešu valoda
Latviešu valoda Lietuvių kalba
Lietuvių kalba Lëtzebuergesch
Lëtzebuergesch Македонски јазик
Македонски јазик Malagasy
Malagasy Bahasa Melayu
Bahasa Melayu മലയാളം
മലയാളം Maltese
Maltese Te Reo Māori
Te Reo Māori मराठी
मराठी Монгол
Монгол ဗမာစာ
ဗမာစာ नेपाली
नेपाली Norsk bokmål
Norsk bokmål پښتو
پښتو فارسی
فارسی Polski
Polski Português
Português ਪੰਜਾਬੀ
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ Română
Română Русский
Русский Samoan
Samoan Gàidhlig
Gàidhlig Српски језик
Српски језик Sesotho
Sesotho Shona
Shona سنڌي
سنڌي සිංහල
සිංහල Slovenčina
Slovenčina Slovenščina
Slovenščina Afsoomaali
Afsoomaali Español
Español Basa Sunda
Basa Sunda Kiswahili
Kiswahili Svenska
Svenska Тоҷикӣ
Тоҷикӣ தமிழ்
தமிழ் తెలుగు
తెలుగు ไทย
ไทย Türkçe
Türkçe Українська
Українська اردو
اردو O‘zbekcha
O‘zbekcha Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt Cymraeg
Cymraeg isiXhosa
isiXhosa יידיש
יידיש Yorùbá
Yorùbá Zulu
Zulu